Table of Contents
hypoxia
see also:
oxygen content in blood in mls/L = (Hb in g/L x 1.36 x oxygen saturation/100) + (0.03 x PaO2 in mmHg)
introduction
- hypoxic hypoxia can be arbitrarily defined as arterial oxygen partial pressure of less than 80mmHg in room air
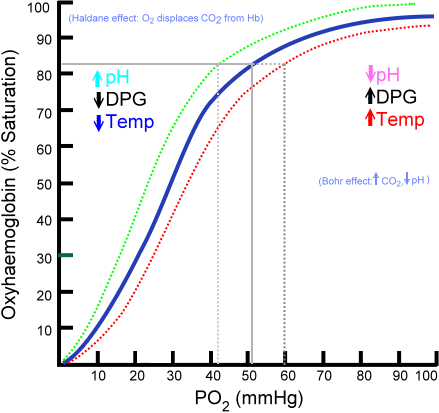
- an arterial PO2 < 60mmHg indicates respiratory failure as, at oxygen levels below this, the Hb-oxygen dissociation curve is steep which means that the ability for Hb to carry much oxygen to the tissues is markedly diminished, as it evolved to be off-loading oxygen to the tissues at these pressures.
- pO2 of 60mmHg equates to an oxygen saturation of less than 90% (see Hb-oxygen dissociation curve - see wikipedia)
- other causes of “hypoxia” or insufficient cellular oxygen usage include:
- anaemic hypoxia - insufficient haemoglobin to carry the oxygen in the blood
- impaired oxygen delivery due to carbon monoxide poisoning or methaemoglobinaemia
- ischaemic hypoxia due to impaired blood flow such as from either blockages, vasoconstriction or venous stagnation
- histotoxic hypoxia due to impaired cellular utilisation of oxygen such as with cyanide poisoning
- the following assumes we are discussing hypoxic hypoxia
alveolar gas equation
- an understanding of this equation if critical in emergency medicine
- each minute, a human at rest consumes ~4ml oxygen per kg body weight and produces ~3ml carbon dioxide per kg body weight
- the ratio of CO2 produced to oxygen used is the “respiratory quotient”
- normal alveolar ventilation = 5L/min in adults with a tidal volume approx. 500ml (7ml/kg)
- FiO2 = fraction of oxygen in inspired gas
- for room air, this is 0.21, for 100% oxygen, this is 1.00
- Patm = atmospheric pressure = 760mmHg at sea level (approx) = 101kPa = 12.8 psi
- Pwater = saturated water vapour pressure at body temperature and at prevailing atmospheric pressure = 47mmHg
- PaCO2 = arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure in mmHg (normal ventilation = 40mmHg)
- RQ = respiratory quotient = 0.8 for most people
- if FiO2 is low, the equation can be simplified by approximating FiO2 x (1-RQ) = 0
alveolar PO2 = FiO2 x (Patm - Pwater) - (PaCO2 x (1-FiO2[1-RQ]))/RQ
Alveolar-arterial gradient
- another essential concept to understand in emergency medicine
- an increased A-a gradient suggests their is a pulmonary oxygen transfer aetiology to hypoxia such as impaired diffusion, V/Q mismatch, or right-to-left shunt
- normal range is 5-20mmHg, increasing by 1mmHg for every decade in age
A-a gradient = alveolar PO2 as determined from the alveolar gas equation - actual measured arterial PaO2
causes of hypoxic hypoxia
low inspired oxygen levels
- high altitude
- enclosed spaces
hypoventilation
- in this case there is a rise in arterial PCO2 levels
- obstructed airway
- decreased conscious state - eg. stroke (CVA), toxicology
- exhaustion from work of breathing
- painful breathing - shingles, pleurisy, fractured ribs, etc
- muscle paralysis - toxinology, neuro-muscular blockers, neuropathies
- chest wall pathology or injury
impaired pulmonary oxygen transfer
- pulmonary fibrosis
- congenital heart disease with right to left shunt
- other pulmonary pathology
Rx of hypoxic hypoxia
- ensure adequate airway and ventilation
- may require positive pressure ventilation such as BiPAP or via intubation
- increase FiO2 as needed
- improve lung function
- Rx the cause where possible
- in suitable patients, when severe hypoxic hypoxia persists despite the above:
- consider ECMO
- in the future, whilst awaiting ECMO, we may be able to give an immediate iv infusion of John Kheir's idea of oxygen filled nanoparticles which seem to work in preliminary testing