Table of Contents
oxygen
see also:
introduction
- once it was thought you could never have too much oxygen, but it has become clear that excessive levels of oxygen can be detrimental, particularly to ischaemic tissues (eg. in acute myocardial infarction (AMI/STEMI/NSTEMI)) and to neonates
- supplemental oxygen needs to be carefully used in certain patient groups, for example, those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are chronic CO2 retainers and rely on their hypoxic drive to stimulate breathing must have their FiO2 carefully adjusted to avoid removing some degree of hypoxia - hence the use of the Venturi mask which can deliver a set FiO2 irrespective of oxygen flow rate.
use of supplemental oxygen in the ED
known or suspected CO2 retainers (eg. COPD)
- target SaO2 is usually 88-92%
- use Venturi mask to ensure exact concentration of oxygen is delivered to avoid excessive oxygen delivery and risk of CO2 narcosis from withdrawal of hypoxic drive
- these patients should be closely monitored to ensure severe hypoxia or excessive oxygenation does not occur
most other patients
- target SaO2 is usually 92-25%
- give oxygen via Hudson mask or Venturi to achieve target level (nasal cannula can be used if flow < 4L/min)
- if > 6L/min is required, consider heated humidified oxygen
potential adverse effects of supplemental oxygen
- type 2 respiratory failure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who are chronic CO2 retainers and rely on their hypoxic drive
- however, patients with PaCO2 < 45 mmHg, receiving oxygen just sufficient to raise PaO2 to 60 mmHg, will be unlikely to experience significant CO2 retention
- reduced ability to monitor ventilation as SaO2 monitors can give high readings for some time when on high FiO2 even though ventilation may have become inadequate
- risk of secondary oxygen radical damage in ischaemic tissues
- reabsorption atelectasis
- prolonged high concentration oxygen in neonates may cause pulmonary toxicity, bronchopulmonary dysplasia and permanant blindness (retrolental fibroplasia or retinopathy of prematurity (ROP)), etc
- oxygen toxicity is a major issue with scuba divers in whom hyperbaric levels may cause seizures, etc.
some important equations
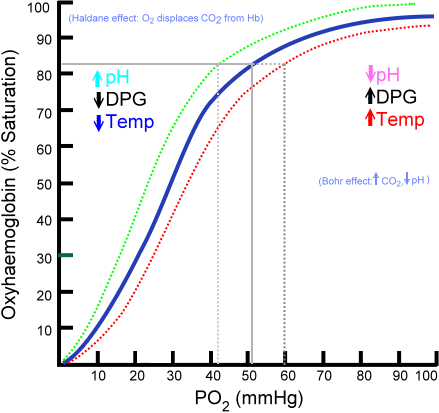
- SaO2 levels relate to PaO2 levels and the Hb-oxygen dissociation curve:
oxygen content in blood in ml/L = (Hb in g/L x 1.36 x oxygen saturation/100) + (0.03 x PaO2 in mmHg)
- PaO2 level is determined by:
- the A-a gradient (thus is generally 5-20mmHg less than the alveolar PO2, but higher if pulm. shunting, etc)
- the alveolar PO2 which is determined by the alveolar gas equation:
alveolar gas equation (simplified for low FiO2 levels):
alveolar PO2 = FiO2 x (Patm - Pwater) - (PaCO2 x (1-FiO2[1-RQ]))/RQ
- FiO2 = fraction of oxygen in inspired gas
- for room air, this is 0.21, for 100% oxygen, this is 1.00
- Patm = atmospheric pressure = 760mmHg at sea level (approx) = 101kPa = 12.8 psi
- Pwater = saturated water vapour pressure at body temperature and at prevailing atmospheric pressure = 47mmHg
- PaCO2 = arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure in mmHg (normal ventilation = 40mmHg)
- RQ = respiratory quotient = 0.8 for most people
oxygen delivery methods
intranasal oxygen
- traditionally has been very useful for delivering 24-40% FiO2 although actual FiO2 is dependent upon various factors such as:
- oxygen flow rate (FiO2 ~ 20% + (4 x oxygen flow rate in L/min if 100% oxygen flow) )
- breathing rate
- tidal volume
- degree of mouth breathing
- other factors
- it is now also recommended during rapid sequence induction (RSI) for emergency intubation to help reduce risk of hypoxia during intubation
- excessive flow rates will dry out the nasal mucosa and be uncomfortable
- usual flow rate is 2L/min but can range from 1-6L/min
- generally better than a simple mask as it:
- is more comfortable
- allows eating and drinking
- avoids rebreathing even at low oxygen flow rates
- oxygen concentrator devices
- these can usually output around 90% oxygen at flow rates of 1L/min, 70% at 2L/min, 50% at 4L/min, and 35% at 5L/min
- thus at 1L/min 90% oxygen will give around 24% FiO2 which may suffice to get alveolar oxygen from 100mmHg to 120mmHg at normal respiration
- these have the advantage over oxygen cylinders of being safer, more portable and can run 24hrs/day without running out (as long as you have electricity), in comparison a C size medical oxygen cylinder of 460L will only last around 4hrs at 2L/min.
simple oxygen mask
- “low-flow” mask with holes in the mask to allow some air entrainment on inspiration, thus if used at 2L/min oxygen flow, inspiration will entrain a further 3L/min air to give the required 5L/min minute ventilation
- should be used at oxygen flow rates of 5-10L/min which delivers FiO2 of 40-60%
- at low oxygen flow rates <5L/min, significant rebreathing may occur because exhaled air is not adequately flushed from the face mask, thus relatively low FiO2 is not able to easily achieved safely
- should generally NOT be used on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with chronic CO2 retention - use a Venturi instead
- mainly used to deliver nebulised medications, or in type I respiratory failure
Venturi mask
- uses the Venturi effect to entrain air at rates in proportion to the oxygen flow thereby keeping FiO2 at relatively constant levels depending on the device
- 24% (4 LPM); 28% (4-6 LPM); 31% (6-8 LPM); 35% (8-10 LPM); 40% (10-12 LPM);
- “high flow” - air is entrained via the Venturi device itself, not through the mask holes as these are there to allow the excess air/oxygen to escape
- even at low oxygen flow rates of 2L/min using a 24% device, the total flow into the mask may be ~40L/min - hence “high flow”
- rebreathing of expired gas is not a problem because the mask is flushed by the high flow rates
- this allows safer application to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with chronic CO2 retention as the FiO2 can be restricted to avoid complete removal of the hypoxic drive but high enough to minimise end-organ hypoxia (ie. aim for a PaO2 of 60mmHg ~ SaO2 88-90%)
Non-rebreathing face mask with reservoir and one-way valve
- allows FiO2 > 40% and up to 90% FiO2
- usually used with oxygen flows of 8-10L/min into the reservoir bag
- should NOT be used on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with chronic CO2 retention - use a Venturi instead
- requires tight seal with the face to achieve high FiO2 levels
partial rebreathing mask
- used in the Rx of acute hyperventilation to raise PaCO2 back towards normal
- usually have a large volume (eg. 2L) reservoir bag
- patient re-breathes their own exhaled air with increasing levels of inspired CO2 until their condition resolves
- requires monitoring